The Future of Web Development: Is the Remix Framework Leading the Way?
Remix, the new framework for developing JavaScript projects with server-side rendering
Table of contents
- Introduction
- What exactly is Remix and why is it awesome?
- So what is Remix?
- So why do we need Remix then?
- Remix vs Next js
- How to initialize a new Remix application?
- 1. Make sure you have Node.js and npm installed on your system.
- 2. Open a terminal and navigate to the directory where you want to create your new project.
- 3. Navigate to the directory where you want to install your remix project:
- 4. Start to create your Remix app and Run the following command:
- 5. Answer the questions with the following:
- 6. Open the index.jsx file:
- 7. Now to see this in action, you should open the terminal.
- 8. Start the development server by running the following command:
- 9. Open up http://localhost:3000, and the app should be running.
- Conclusion
Every day, new frameworks and tools are introduced to the developer community. Some of them take a novel approach to solving issues that are currently being addressed by existing tools. Others contribute a new thought or idea, presenting a new approach to the initiatives. A mechanic has numerous tools for different tasks, developers have multiple frameworks and libraries that are suitable for various use cases.
Let's speak about Remix, the new kid on the block, a new framework for developing JavaScript projects with server-side rendering. Let's go over its key features and concepts, as well as the similarities and differences between it and another prominent JavaScript framework: Next.js. Let’s also Initialize a Remix application and see how easy it is. And in the end, if you got hooked I added two Link tutorials you can follow along.
Introduction
In this article, you will learn how to use Remix,, a React framework, you will learn what exactly Remix is and why it's amazing, you will learn all the basics, and more advanced features with some tutorial links, and therefore let's not waste any time.
Let's step right in, and let's start with that most important question.
What exactly is Remix and why is it awesome?
But first, check out the prerequisites and recommended tools you should use if you want to get the most out of this article.
Prerequisites
While not completely necessary, I believe you will get the most out of this article if you come up with:
A basic understanding of JavaScript
Some experience working with React
Some experience with the NextJS Framework (not required).
Make sure you have node.js installed on your machine.
If you want to follow the tutorial in the last part of this article locally on your own computer, it is important for you to have these things installed:
Tools you will use
Below are the various tools and technologies you will get to touch with in this tutorial:
Remix, your application framework
CSS framework
Fly.io, as your website hosting provider if you follow the tutorials. mentioned in this article. In one of the tutorials, you're going to use our own SQLite database. Essentially, it's a database that lives in a file on your computer, is surprisingly capable, and best of all it's supported by Prisma, our favorite database ORM! It's a great place to start if you're not sure what database to use.
So what is Remix?
Well, it is a framework for React JS. And that, of course, brings up one important question.
Isn't React JS already a library?
Yes, it is!
You do know for sure that React JS is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces, highly reactive user interfaces to be precise.
So why do we need Remix then?
Well, Remix builds up on top of React JS, so you will still write React code, but Remix adds a lot of extra features that simplify the process of building full-stack applications with React.
Because if you're using Just-React, if you have a normal React project as I have it here in this frontend folder, then you have a lot of code that deals with displaying a user interface.
However, if that application also needs a backend where you, for example, store data in a database, you must add code to that React application that sends requests to that separate backend server, which then runs some server-side code that does actually talk to the database.
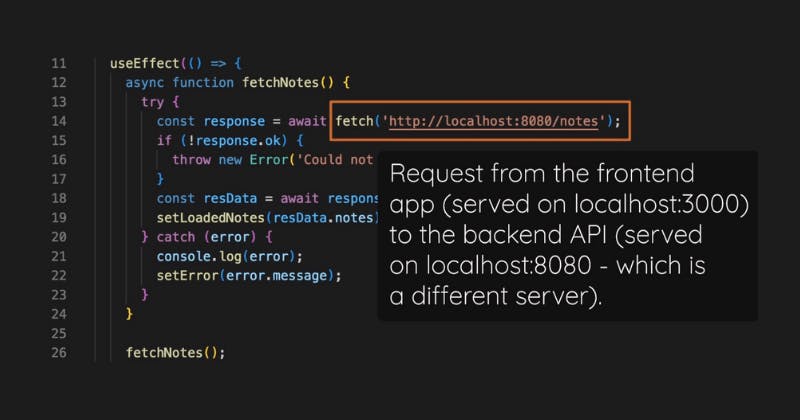
So you have code in your front-end React application for sending requests, managing some loading state while the request is on its way so that you can show some loading spinner or some loading display, and handling any potential problems that may be returned.
That's what you do on the front end.
And as mentioned, what you need then is a separate backend if you wanna build a full-stack application.
So that's a totally different project, for example, built with node and ExpressJS, but you could build it with any programming language.
And there, you then do the actual work of reaching out to a database or to a file or wherever you're storing your data.
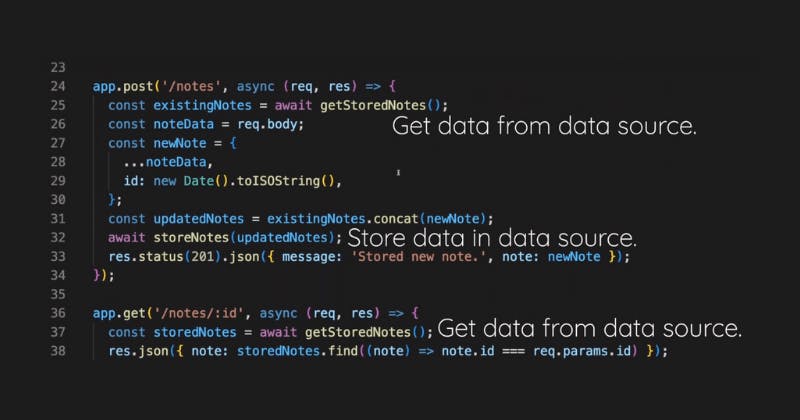
You could build such a backend yourself, or you're using some third-party service like Firebase.
But either way, you have a separate, detached backend.
That's how you usually build full-stack applications when using React for the front end.
And it's critical to understand and remember that in your React app's front-end application, you're not directly talking to a database or anything like that.
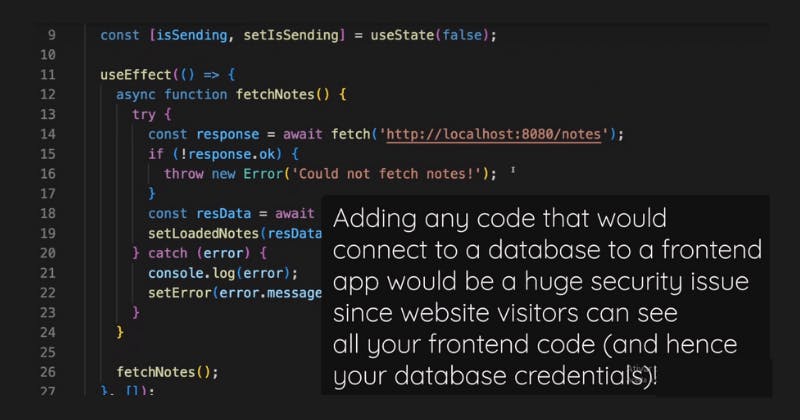
Instead you're sending requests to a separate backend.
That request is now routinely issued using useEffect, which, for example, covers the code for sending such a fetch request.
Or if you're using the latest version of React Router, you could also use the new API offered by React Router for adding loaders and actions for sending requests when a route becomes active, for example.
You still have a separate backend with that, but the React code you have to write gets much easier and cleaner.
Either way, you have a detached backend.
Now, if you are using Remix instead, then these things change.
- You still build a React application, - you still have a React component, - you still write React code,
But you blend your server-side code into the same file where you define your components.
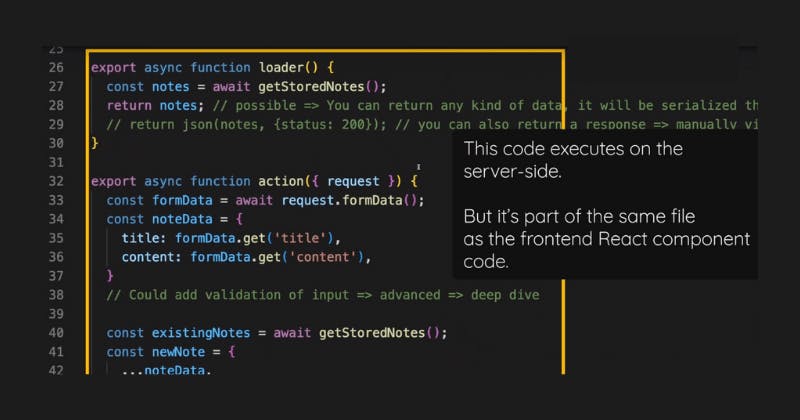
So you have a mixture of front-end and back-end code in the same file.
The code here might look similar to what you saw with React Router since I also have such a loader and such an action function here, but here, we then actually have code that runs on the server, some backend code.
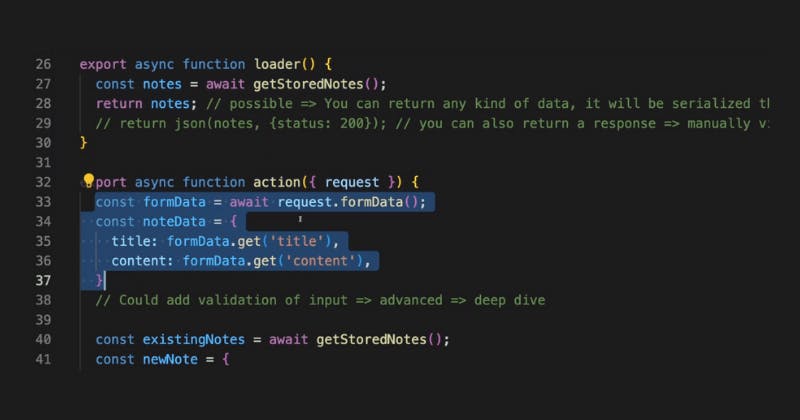
And therefore, of course, building a full-stack React application becomes much easier because you have one project with back-end and front-end code that works together seamlessly.
And Remix automatically splits your code such that only the front-end code is served to your users, so they never see your back-end code, which could also contain sensible data, for example.
On the other hand, the backend code is executed on a server.
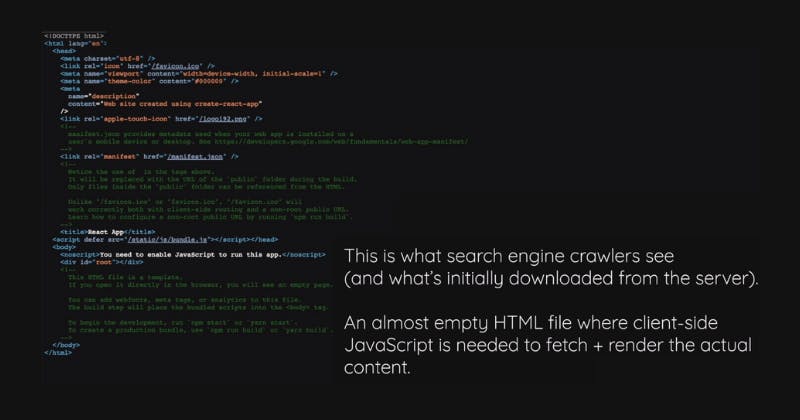
As a side effect that should not be overlooked, the users of your website, or visitors to your website, receive nothing when they visit it.
So they get the finished HTML page with all the data already injected into it, which also helps a lot with search engine optimization.
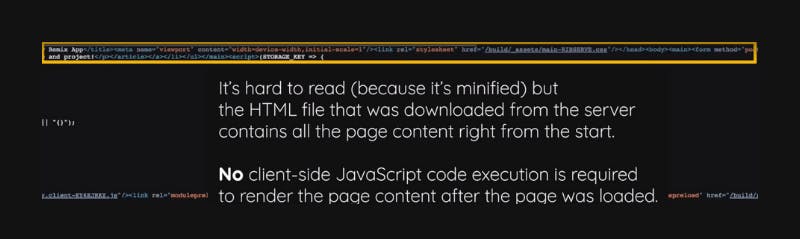
Since those search engine crawlers see the full website, including all the data that makes up that website, instead of just seeing the empty skeleton that is yet to be populated by React, by the client-side code that is yet to execute after the first version of the page has been loaded.
So that's a significant benefit of using Remix because Remix pre-renders all of these components and pages on the server before serving the finished page to your end users.
So that's what Remix is and why you might want to use it. It simplifies the process of building full-stack React applications by merging the code bases and it gives you many advantages, and Remix has a couple of other amazing features.
And to be honest, writing Remix code and building Remix apps is simply a lot of fun because it's such an amazing framework.
Remix vs Next js
Now, previously, you learned what Remix is and why you might want to use it. Now, maybe what you learned there sounds familiar to you. There is another framework for React called Next JS, which aims to solve the same problems; and also helps with building full-stack applications.
But there are some important differences between Remix and Next JS.
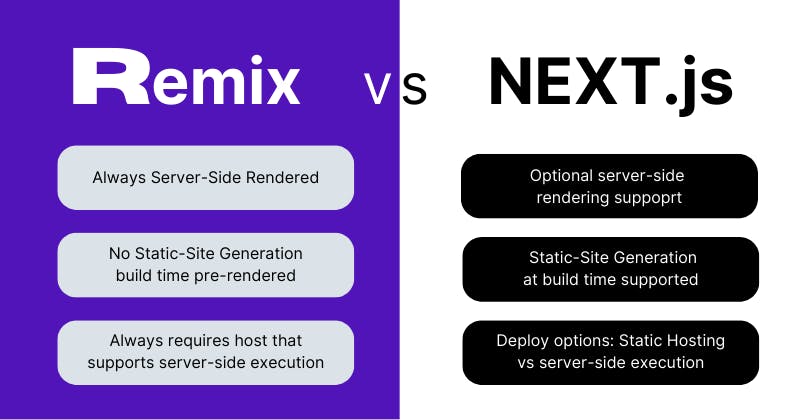
With Remix, you always render all pages on the server. So whenever a user enters a URL leading to your page, that page that's being served is rendered on the server.
So the user always gets the latest data and a brand-new page.
Of course, you can set up some caching if you want, but generally, it is rendered when a user visits the site.
But with Next JS you can write code that forces a page component to be rendered for every request, but this is only optional because most of the time you write code that statically generates the site at build time, so right before deployment.
With Remix, this is not supported, but with Next JS, it is basically the standard or the default for many pages.
As a result, if you want to deploy Remix, you will always require a host, which is a server that supports server-side code execution.
That isn't always the case with Next JS because if you pre-rendered all pages at build time, you only need a static host. You only need a host that's capable of server-side code execution.
For Next JS, if you're using this optional feature of rendering certain pages on the server.
But these are just some technical differences. There also are many syntax differences, and even though I really like Next JS and it is absolutely amazing, I think that Remix has an even nicer API and that building Remix apps is even more fun than it is building Next JS apps, which still is awesome, don't get me wrong, but Remix is maybe more awesome.
How to initialize a new Remix application?
We do that with a command that we execute in the command line, in the terminal.
And it does not matter which operating system you're using, the command is always the same and you'll always build Remix applications in the same way.
Now for this command, which we're about to execute, you must have node.js installed., because the Remix code you write also includes node.js features. Therefore, you should visit nodejs.org and there you can download the latest node.js version. In my case, it's version 19 but you should simply download the latest version you are seeing when you are reading this.
And if that's a later version, that's perfectly fine, what you'll learn here about creating a Remix project, probably will still apply.
Now, after installing node.js, back in the terminal or command prompt, you are ready to run the command to create a new Remix project.
And that command is called npx, which is a command made available by node.js, after npx add create-remix, and then to be safe that you're using the latest version of this Remix project creation tool, you should add @latest thereafter: npx create-remix@latest.
To start a new Remix project, follow these 9 steps:
1. Make sure you have Node.js and npm installed on your system.
2. Open a terminal and navigate to the directory where you want to create your new project.
3. Navigate to the directory where you want to install your remix project:
Make sure you are in the folder where you want to create your Remix project. For example, You can start on your MySites Folder or MyProjects folder or something similar.
Let's continue...
4. Start to create your Remix app and Run the following command:
$ npx create-remix@latest
This will create a new directory called
my-remix-appand install the necessary dependencies for a Remix project inside it.
But, first, after you run npx create-remix@latest -> ENTER this will now take a short while until it gets started and then it will ask you a couple of questions and scaffold the beginnings of a Remix application for you.
5. Answer the questions with the following:
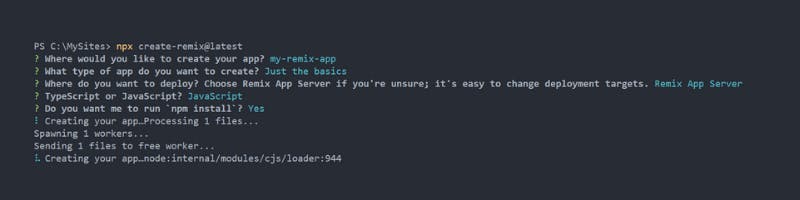
Where would you like to create your app?:
my-remix-appWhat type of app do you want to create?:
Just the basicsWhere do you want to deploy?:
>Remix app serverTypeScript or JavaScript?:
JavascriptDo you want me to run
npm install?:Yes
Now let's just wait a couple of minutes till the installation is finished. And once the installation is finished and the project is therefore created, you can open it with your favorite code editor. In my case, that's Visual Studio Code, but you can use any code editor you want.
And with that project created, it's now time to take a closer look at your app folder app/routes/index.jsx
6. Open the index.jsx file:
And we start with one single file in there right now, the index. jsx file, which basically is our homepage, the starting page of this website.
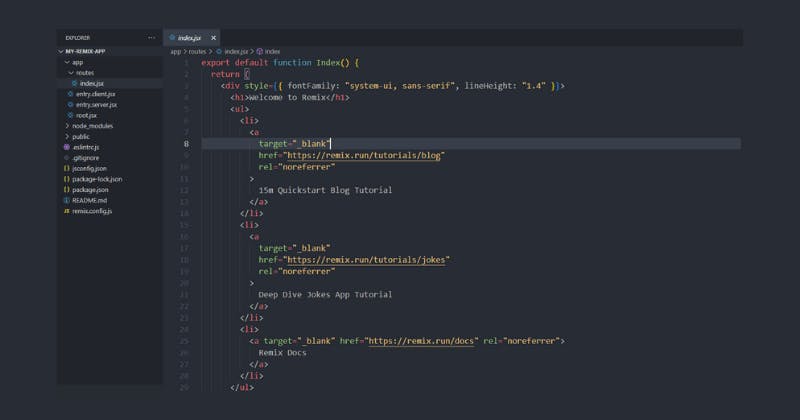
You will get some dummy content in there, and the exact content might change over time. So when you create a new Remix project, this content might be different.
7. Now to see this in action, you should open the terminal.
I'm using the one integrated into Visual Studio Code, but it's still my default terminal.
8. Start the development server by running the following command:
$ npm run dev
9. Open up http://localhost:3000, and the app should be running.
http://localhost:3000
This will start the development server and open a new browser window with your Remix application. The development server will automatically reload the page whenever you make changes to your code, so you can see your updates in real time.
Note that: create-remix is a command-line tool that generates a new Remix project based on a template. You can customize the template by providing additional options when creating your project. For example, you can specify a different version of the Remix framework or use a different template. To see the available options, you can run:
$ npx create-remix --help
The website, as previously stated, would display some dummy content in the form of two lesson links. One brief blog instruction and one lengthy full-stack jokes app tutorial.

I strongly encourage you to do one of the tutorials before anything else. These lessons will show you how to start with web basics and gradually improve your app to obtain the modern UX you desire.
If you work through the blog tutorial with Kent in this free Egghead.io course, you'll learn how to take full advantage of what Remix has to offer. You will learn by creating a fully functional blog that includes a database, authentication, CRUD operations, user roles, and more!
Conclusion
Congratulations, You've finished reading this article and learned some of the main characteristics of the Remix framework. You learned some of the essential differences between using Remix and Next JS and therefore you have all you need to start building your own Remix applications and dive deeper into Remix. And definitely keep on using Remix. Keep on practicing Remix, building demos, and doing dummy projects because that is how you will learn the most.
Definitely also try rebuilding these course projects without looking at the tutorial you are attending, because that can be great practice as well because ultimately, tutorials show how it is done, You then need to practice what you saw and learned, so that you can really grow and learn more and more about Remix and web development in general.
That being said, I hope you liked the article, and I also hope you got a lot out of it.

